Definition Hardware Fault Tolerance
The ability of maintaining functionality when portions of a syste.
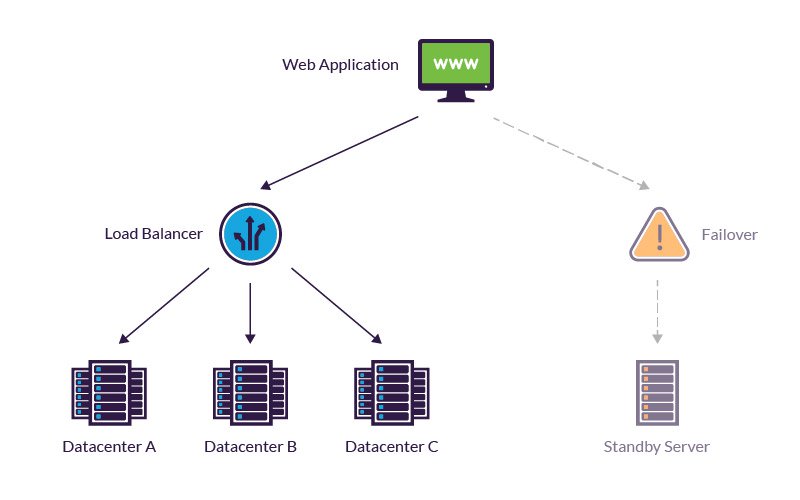
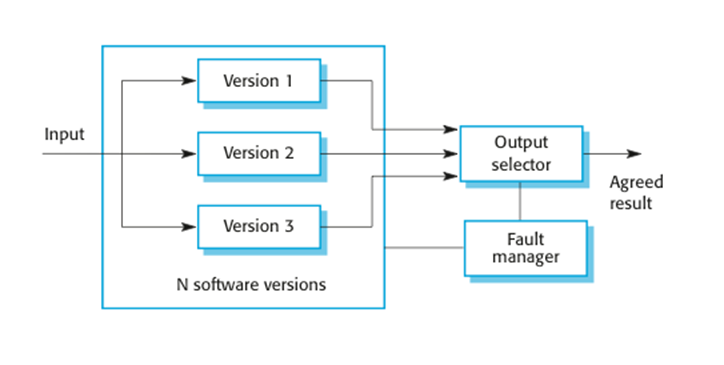
Definition hardware fault tolerance. This is true whether it is a computer system a cloud cluster a network or something else. Fault tolerance simply means a system s ability to continue operating uninterrupted despite the failure of one or more of its components. In other words fault tolerance refers to how an operating system os responds to and allows for software or hardware malfunctions and failures. Many hardware fault tolerance techniques have been developed and used in practice in critical applications ranging from telephone exchanges to space missions.
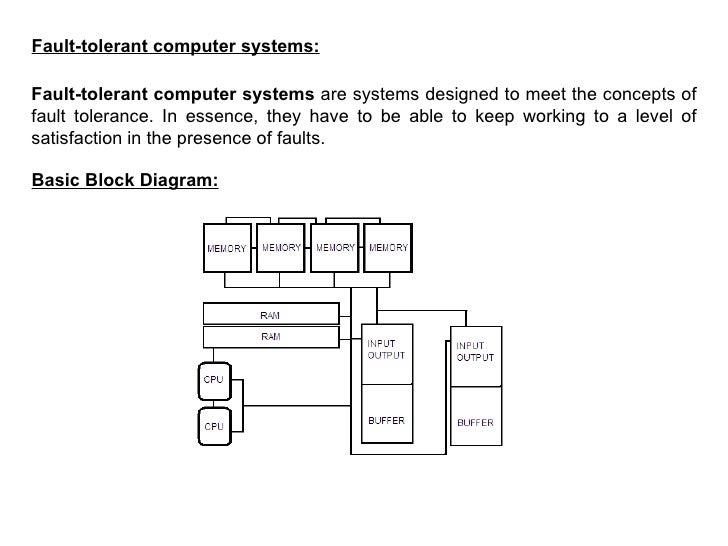
Fault tolerance is the property that enables a system to continue operating properly in the event of the failure of some of its components. What is fault tolerance. Fault tolerance is the way in which an operating system os responds to a hardware or software failure. Hardware fault tolerance is the most mature area in the general field of fault tolerant computing.
If its operating quality decreases at all the decrease is proportional to the severity of the failure as compared to a naively designed system in which even a small failure can cause total breakdown. Fault tolerance is particularly sought after in high availability or life critical systems. Fault tolerant technology is a capability of a computer system electronic system or network to deliver uninterrupted service despite one or more of its components failing. A system can be described as fault tolerant if it continues to operate satisfactorily in the presence of one or more system failure conditions.
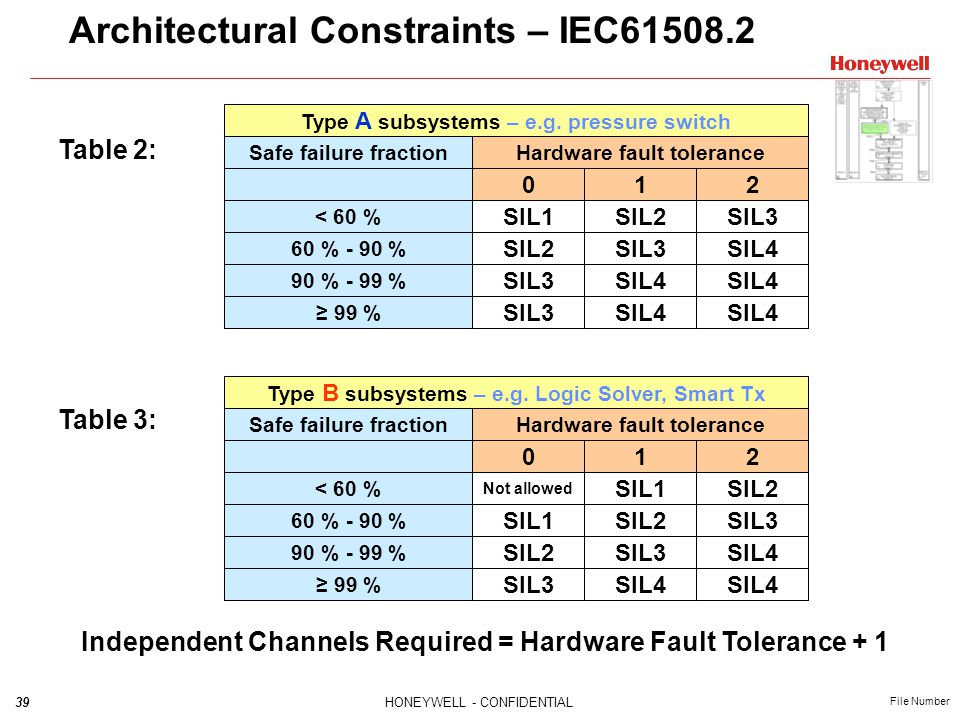
Fault tolerance refers to the ability of a system computer network cloud cluster etc to continue operating without interruption when one or more of its components fail. Hardware fault tolerance is the ability of a component or subsystem to continue to be able to undertake the required safety instrumented function in the presence of one or more dangerous faults in hardware. Fault tolerance also resolves potential service interruptions related to software or logic errors.